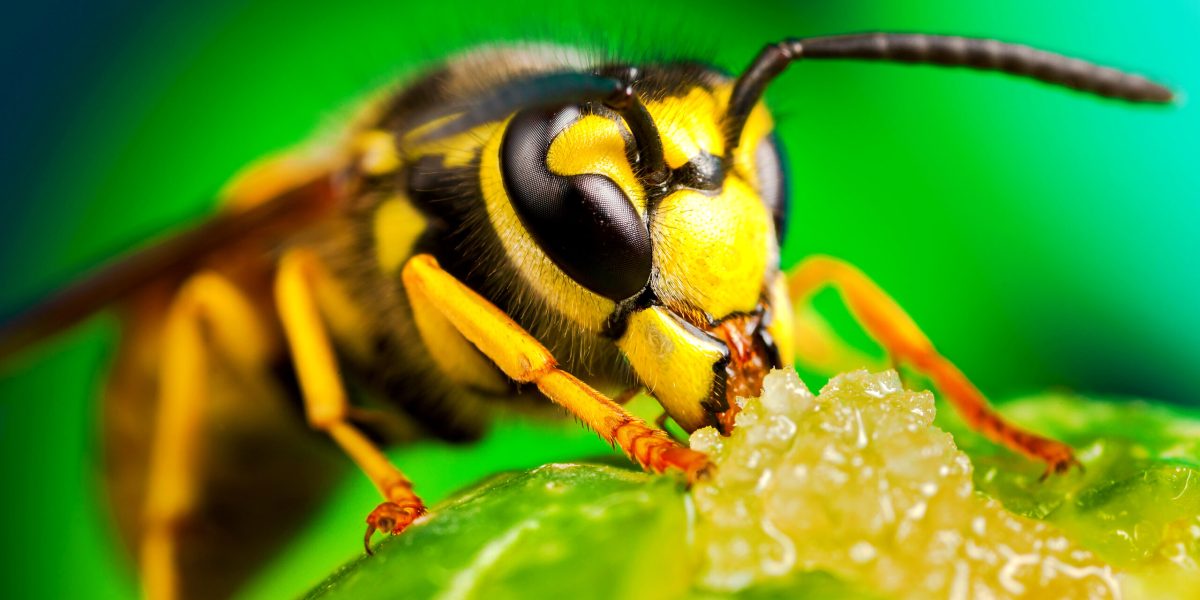
Trying to decide if you need to remove a wasp nest? Read on to see what options you have if it must be removed. Killing off a wasp nest is tricky business. As many of us know, wasps can be quick to sting people who approach their nest.
Deciding if you need to remove a wasp nest
Many species of wasps provide beneficial ecosystem services such as feeding on garden pests. Wasp nests that don’t pose an immediate hazard can be left alone. Wasps vacate their nest in the fall and don’t reuse the same nest the next year. After a couple of hard frosts, the wasps should no longer pose an issue. Leaving wasp nests alone may reduce insecticides in the environment and support beneficial insects.
Professional pest removal companies can remove wasp nests that pose a threat to humans, pets or livestock. Anyone who attempts to use insecticides for wasp nest removals should follow the pesticide’s label and take precautions to avoid stings or other injuries.
Many species of wasps, bees and even flies can look alike to the untrained eye. Begin by confirming that you are dealing with social wasps by reviewing insects that look like bees from Michigan State University Extension (MSU Extension)
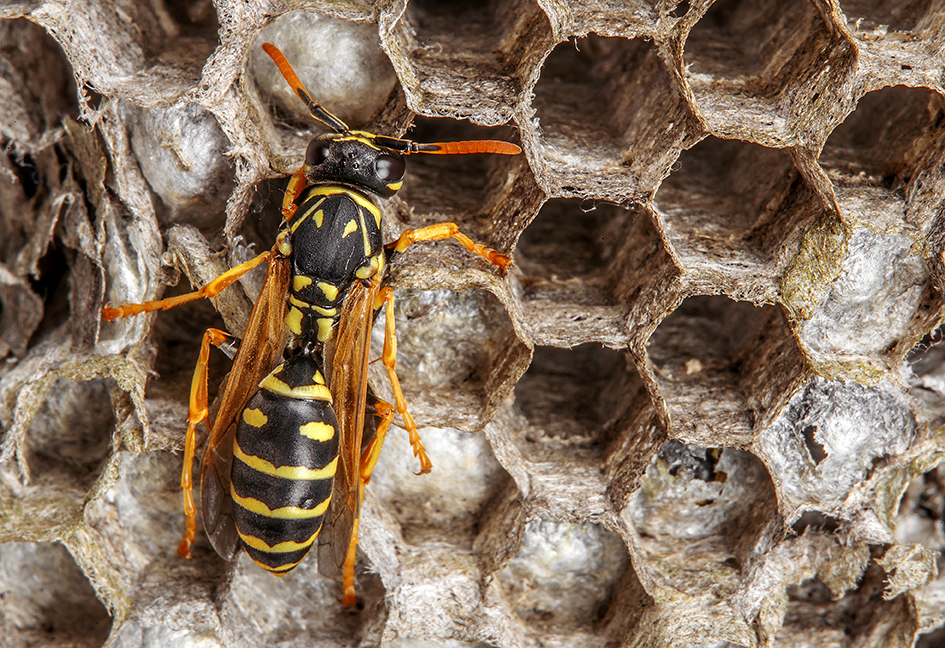

Seasonal life cycle of wasps
The wasps that may become a nuisance in late summer and fall belong to the family Vespidae. Though many species of vespids lead a solitary lifestyle and rarely cause us problems, yellow jackets, bald-faced hornets and paper wasps are social insects that live in large colonies. They construct their nests in the ground, in trees, under eaves and inside wall voids and attics.
SPRING & SUMMER
During August, the colony reaches its maximum size of worker wasps. The maximum size depends on the species; paper wasps may only produce a few dozen workers, while colonies of yellow jackets may reach one or 2,000 wasps.
FALL & WINTER
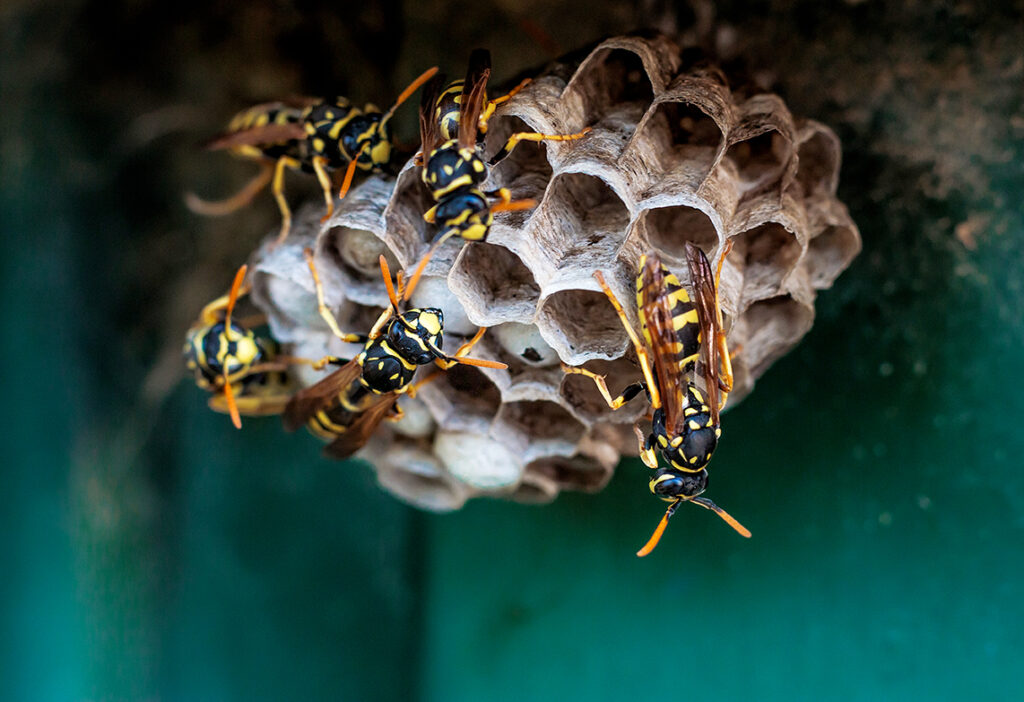

Removing wasp nests
small, exposed nests of paper wasps
yellow jackets and bald-faced hornets Nests
Yellow jacket ground nests
In instances where the nest must be removed, ground nests are easily controlled with a single application of an insecticidal dust directed at the nest opening. Insecticidal dusts work well in these cases because the wasps pick the dust up as they enter the nest and carry it to the core of the nest. This insecticide contaminates the entire nest and soon all the wasps will die off, normally within one or two days. Early morning is the preferred treatment time and the precautionary measures outlined in the above paragraph should be followed. Apply an insecticidal dust with a disposable paper cup or bulb duster. Then, quickly dump the cup or bulb duster directly in the nest opening and move away from the nest with great haste.
Nests inside structures
If you discover yellow jackets nesting inside your home, you can choose to ignore it or call a pest control company to destroy it. Do not plug the outside opening of these nests because this will force the wasps to chew their way into the interior of the house, and this is never a good thing. Pesticides applied in these situations must name buildings or structures as allowable application sites on their labels.
Ana Heck and Nate Walton,
![]()
Michigan State University Extension